Sanitation systems where the sewer does not go, DEWATS are the sweet spot between waterless on-site sanitation and conventional sewers with centralised wastewater treatment.
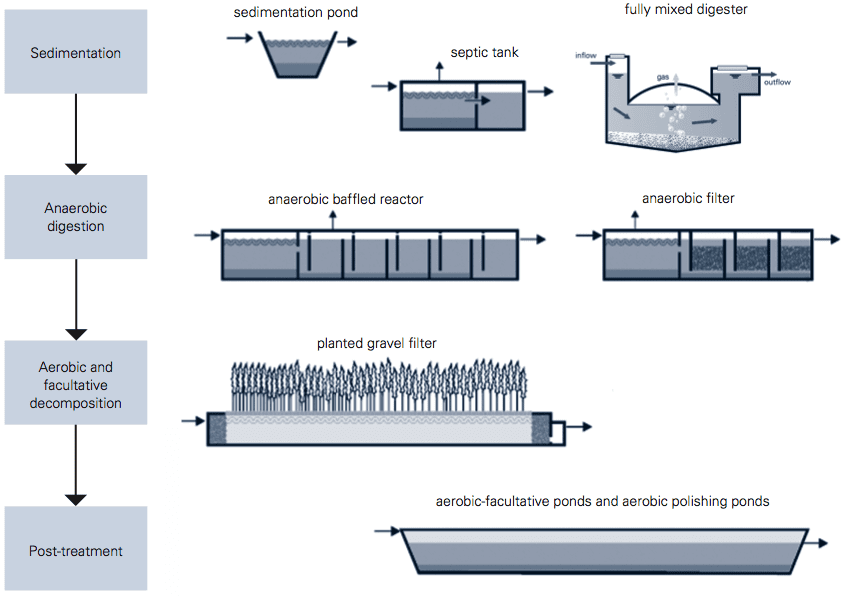
Decentralised Wastewater Treatment Solution What is DEWATS?Decentralised Wastewater Treatment Systems (DEWATS) is a combination of biological treatment procedures to purify wastewater to a standard that allows for safe disposal into natural water bodies or for use in agriculture. Wastewater treatment efficiencies can be controlled according to the governmental regulations of the place of implementation. Stages in a typical DEWATS?
| Step | Module | What is it really? |
| 1 | Inlet chamber | The wastewater from the area being serviced flows through this common point, therefore DEWATS is always at the lowest point of the site. |
| 2 | Screen chamber | Built to suit the municipality, this chamber prevents anything larger than 20 mm in diameter to enter the treatment system |
| 3 | Settling chamber | A physical separation occurs in this chamber. The heavier particles sink, the fats and oils combine and float on the surface, and finally the suspended layer in between flows through to the next chamber. |
| 4 | Anaerobic Baffled Reactor (ABR) | An advanced septic tank that is designed to retain wastewater for longer periods, determined by the treatment efficiency requirement. Within the chamber, a maze of walls are set up, forcing extended periods of contact between settled sludge and fresh wastewater. This assists with overall purification of the wastewater. |
| 5 | Anaerobic Filter (AF) | The chamber is set up to force wastewater to flow through a membrane of material that further enhances the treatment. The membrane is very easy to construct (any non-porous material that ranges between 30 – 60 mm in diameter). |
| 6 | Mechanical Siphon | This is a device that pumps wastewater onto the constructed wetlands of DEWATS. The pump achieves flow rates of 75 ℓ/s and works off the principal of buoyancy. No electricity needed and it is built right here in South Africa. |
| 7 | Stage 1 – Constructed Wetland, with vertical filtration | The first stage of advanced treatment is a course gravel filter, where the focus is on mechanical and biological post-treatment for organic pollutants (COD/BOD), ammonia and nitrate. |
| 8 | Stage 2 – Constructed Wetland, with vertical filtration | Before this stage, another mechanical siphon is set in place to ensure that wastewater is effectively distributed on the surface of the second wetland. This filter uses fine sands and the focus here in addition to nitrogen removal is pathogen removal. |
Secondary Treatment = Anaerobic Baffled Reactor (ABR)
Tertiary Treatment = Planted Gravel Filter + Polishing Pond Can treat 1 – 1500 m3 of wastewater a day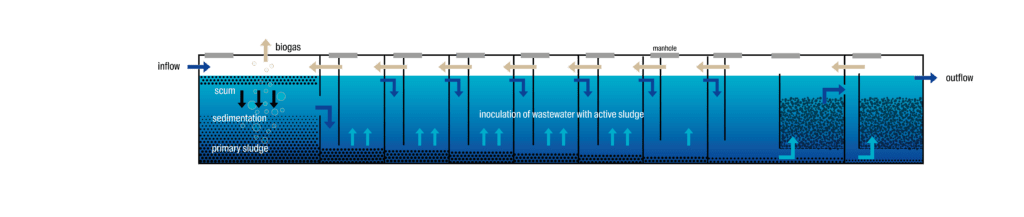
- Individual households
- New and existing settlements
- Institutions
- Schools
- Hospitals
- Small and medium-sized enterprises
- Local materials, minimal scrap value
- Simple to operate and maintain
- Reduced pipe lengths, fewer pump stations
- No electricity or chemical inputs required low operating costs
- Can be placed in or near community
- Beneficial reuse: treated effluent, biogas, urine








